Lab One Observing and Measuring
Earth Materials and Processes
·
Objectives:
1) Identify and describe earth materials and processes
2) Measure and calculate length, area, volume, mass and
density
3) Develop and test physical and quantitative models of isostasy based on floating wood blocks and icebergs…apply
to the earth
4) Analyze earth’s global topography and the hypsographic
curve- related
to isostacy??
· Two kinds of Data…
Qualitative-
Observations and
Descriptions
Quantitative- Data obtained by measuring
changes in time and space.
·
Measurements and
Conversions…
Linear Measurements: One
dimensional measures of lengths and distances.
ex-
The distance from
Area Measurements: Two dimensional measures of
space.
ex- A field is
10ft wide and 5ft long (linear measures) so the field occupies an area of 10ft x 5ft = 50ft2
Volume Measurements: Three
dimensional measure of the space an object occupies.
ex- A cube has
a length of 5cm, a height of 10cm and a width of 2cm…so the volume the cube
occupies in space is L x W x H
or 5cm x 10cm x 2cm = 100cm3
OR
To
find the volume of an irregularly shaped solid, use a graduated cylinder and
determine how much water the object displaces, that is its volume. convert ml to cm3
1ml = 1g = 1cm3
Conversions…
converting one unit to another ie. cm to m
cross canceling units-
convert 4300ft to miles then
km…
4300ft x 1mile x 1km =
1.31km
1 5280ft .6214mile
Mass: Measure of how much an object weighs in
earth’s gravity.
ex- 4ml of
water weighs 4g (from conversion above)
Density: Measure of an objects mass per unit of
volume…reported in g/cm3
ex- A rock has
a mass of 45g and occupies a volume of 30ml…
So- first convert 30ml to cm3 30ml x 1cm3 = 30cm3
1 1ml
Then- put mass over volume and divide…
45g / 30cm3 = 1.5
g/cm3
Questions so far…………….
Buoyancy and
Isostasy….
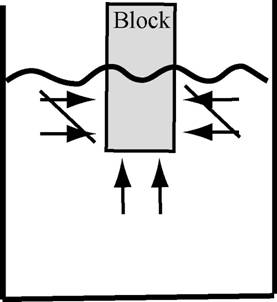
Buoyancy: Why does
a block of wood float in water??
A fluid, like water, pushes in all directions…
When an object, like a wood
block is placed in water- the water pushes on its sides in all directions…
The opposing forces on each
side of the block cancel each other and the only force that is left is a force
pushing upward on the bottom- the buoyant force
Isostasy:
The reason an object floats
is that it displaces an amount of water equal to the weight of the object- allowing
the buoyant force to support the object.
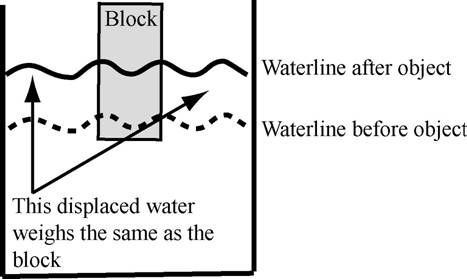
Definition: Isostasy is the
balancing condition between the object and the displaced water.
·
How high out of
the water an object floats is determined by its isostasy.
·
A lighter
material will float higher because it doesn’t need to displace as much water to
float, allowing it to rise above a denser material that must displace a greater
amount of water, causing it to sink lower.
To Determine Isostasy you will need….
HTotal The total
height of the block
HBelow The height of block below waterline
HAbove The height
of block above waterline
rwater The density of water
rblock The density of wooden block
look at fig 1.16
Now,
Think about these principles
applied to the earth, remembering that the continental crust is composed of
less dense materials and the oceanic crust is composed of more dense materials.
Some Terms-
Bimodal?? Means two peaks on a graph see fig 1.17 on pg. 26
Hypsographic??
A graph on page 26 that shows height in km on the y axis and the percent
of the earth at that height on the x axis
Show all Work and Units All the time