Lab 7 Metamorphic Rocks
What
is a Metamorphic Rock?
-rock changed by heat, pressure or
fluids
Parent
Rock (Protolith)
-The original rock type before it
underwent metamorphism
Two
types of Metamorphism:
1)
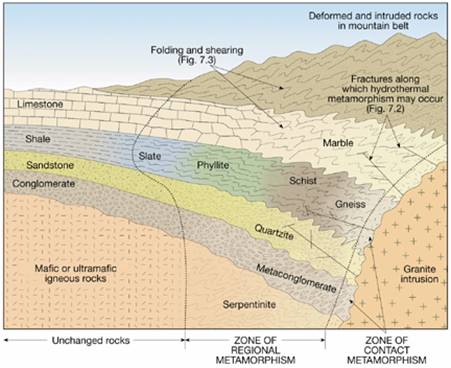
Contact Metamorphism-
- rocks that are close to
an igneous intrusion, like a batholith, undergo metamorphism from the heat and
fluids given off by the intrusion.
2)
Regional Metamorphism-
- large scale metamorphism
of rocks within the crust, like underneath mountain belts, produces regional
metamorphism. Rates of deformation are
very slow, rocks are folded and metamorphosed over a
long period of time.
Metamorphic
Rock Textures:
Foliated
vs. Non-Foliated
-Foliated means a parallel alignment of platy
minerals like mica. The rock appears
layered, with “stripes” of crystals
· Foliated Metamorphic Rock Textures-Increasing met. grade
Slaty Rock Cleavage-
-Microscopic faults within the rock produce a sheet
like cleavage. Slate is a good example
of a metamorphic rock with slaty cleavage.
Phyllite Texture-
-Rock has a shiny luster (sheen) resulting from the
growth of platy micas. The surface of
the rock may be wrinkled and wavy. Intermediate grade.
Schistosity-
-Mica minerals are visible to the naked eye, rock appears to have scales and is very
reflective. Intermediate
to High grade.
Gneissic Banding-
-Alternating layers, or lenses, of light and dark
minerals. Mafic minerals usually form
the dark bands, and felsic minerals usually form the light colors.
· Non-Foliated Metamorphic Rock Textures-
-Crystalline Texture
-Med to coarse grained
aggregate of intergrown xtals
-Microcrystalline Texture
- very
fine grained aggregate of minerals
-Sandy Texture- (not sedimentary)
- A sandstone that has undergone metamorphism would
have a sandy texture, the grains would be
recrystalized and interlocking. Ex-
quartzite
Textures
that occur in any Metamorphic Rock-
-Stretched or Sheared Grains-
-deformed grains (pebble, fossil etc) are stretched
out like putty
-Folds
-Initially linear features can be bent and buckled
into a folded geometry
Many more on Page 140
· Classification of Metamorphic Rocks:
-Metamorphic rocks are named based
on their texture and mineralogical compositon…
ex- A rock that has
large, visible grains of muscovite mica roughly aligned in a foliation with
small garnets would be called a-
Garnet Schist
Name then Texture
If
more than one accessory mineral list in order from least to most abundant.
Ie. If the above described rock were to have a
small amount of biotite then you could call it a Biotite Garnet Schist