Brief Timeline of American
Literature and Events
1750-1799
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Brief Timeline of American
Literature and Events
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1750-1799 | Political
and Social History |
Literature |
| 1750-1754 | 1750 (22 June) Jonathan
Edwards is dismissed from his Northampton (Mass.) church when he rejects
the liberal
"halfway
covenant." He becomes pastor of a church in the frontier settlement
of Stockbridge, in western Massachusetts.
1754-63 French and Indian War (See history). 1754 Colonies adopt Benjamin Franklin's "Plan of the Union" of English colonies. |
1751. Benjamin
Franklin publishes New Experiments and Observations on Electricity. |
| 1755-1759 | 1758 General Montcalm and his French
troops are defeated at Fort Ticonderoga, New York.
1758 Jonathan Edwards becomes president of the College of New Jersey, later Princeton University. 1759 Quebec surrenders to the British under Wolfe. |
1758 Benjamin Franklin, "The Way to Wealth" |
| 1760-1764 |  1760
Pennsylvania-born painter Benjamin West travels to Italy to study art and
becomes a celebrated artist in London. 1760
Pennsylvania-born painter Benjamin West travels to Italy to study art and
becomes a celebrated artist in London. Benjamin West's Self Portrait (1770) courtesy of Carol L. Gerten (Jackson)'s site at the University of North Carolina.1763 10 February. Treaty of Paris ends the Seven Years War (French and Indian War). France cedes Acadia (Nova Scotia), the St. Lawrence River islands, and Canada to the British. 1764 Boston lawyer James Otis publishes The Rights of the British Colonies Asserted and Proved. |
1760 Ezra Stiles, A Discourse on the Christian Union
1764 James Grainger, The Sugar-Cane, A Poem in Three Books |
| 1765-1769 | 1765 Stamp Act is enacted by English
Parliament and meets with colonial opposition.
1766-67 Daniel Boone travels to the Kentucky territory through the Cumberland Gap. 1769. Fr. Junipero Serra founds the Mission at San Diego and eight others, hastening the colonization of California.(Another biographical sketch.) |
1765-6 William Bartram travels in
Florida with his father, John
Bartram.
1765 James Otis, A Vindication of the British Colonies 1768 Samson Occom, A Short Narrative of My Life 1768 John Dickinson, Letters from a Farmer in Pennsylvania 1768 Milcah Martha Moore, "The Female Patriots. Address'd to the Daughters of Liberty in America, 1768" |
| 1770-1774 | 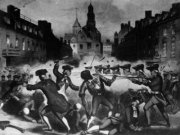 1770.
5 March. When British troops arrive in Boston, they are surrounded by angry
colonists and fire into the crowd, killing three Americans and wounding
two others. The event becomes known as the Boston Massacre. (Image
courtesy of Images
of Political History. See also the Map
of the Americas showing European powers [1774] [262 k. file]) 1770.
5 March. When British troops arrive in Boston, they are surrounded by angry
colonists and fire into the crowd, killing three Americans and wounding
two others. The event becomes known as the Boston Massacre. (Image
courtesy of Images
of Political History. See also the Map
of the Americas showing European powers [1774] [262 k. file])
1773 May 10. Due to pressure from the East India Company, which has suffered because of the colonists' successful embargo on tea, the Tea Act becomes effective. It retains the threepenny tax on tea but repeals the previous export tax, so that British tea merchants can now undercut the prices of American sellers.
|
1770 Robert Munford's satirical play,
The
Candidates; or, The Humours of A Virginia Election
1771-90 Franklin continues writing the Autobiography (Part I published in 1818) 1773 Phillis Wheatley, Poems on Various Subjects 1774 John Woolman, The Journal of John Woolman 1773-1776 William Bartram travels throughout the Southeast, a journey that he later chronicles in his Travels |
| 1775-1779 |
1776 1775-83 Revolutionary War (see timelines for battles and events) |
1775 Mercy Otis Warren, The
Group
1776 Thomas Paine, Common Sense |
| 1780-1784 | 1780
1781 1783-5 Noah Webster's "Blue-Backed Speller" (A Grammatical Institute of the English Language) helps to standardize spelling and to distinguish British from American English. |
1782
J. Hector St. John de Crevecoeur, Letters from an American Farmer
1783 Franklin's Remarks Concerning the Savages of North America |
| 1785-1789 | 1785. March. Thomas Jefferson is appointed
minister to France, replacing Benjamin Franklin.
1786 Congress adopts a decimal coinage system based on the Spanish milled dollar. 1787 Shays's Rebellion in western Massachusetts. Farmers facing foreclosure deny judges entrance to the courthouses where bankruptcy proceedings are heard. In a confrontation at Springfield, four farmers are killed as 1,000 militiamen fend off approximately 1,500 farmers. 1787. 25 May. The Federal Convention convenes in Philadelphia, although only seven states are represented. Several provisions of James Madison's Virginia Plan become part of the U. S. Constitution, including a bicameral legislature, a federal judiciary branch, and an executive branch. The Constitution is approved on 17 September and then is sent to the states for ratification. 1789 George Washington elected president. |
1786 Philip
Freneau, Poems
1787 Thomas Jefferson, Notes on the State of Virginia October 1787-May 1788. The Federalist Papers appear in New York newspapers under the pseudonym Publius. The letters are written by James Madison (1731-1836), Alexander Hamilton (1757-1804), and John Jay (1745-1829). 1789 Olaudah Equiano, The Interesting Narrative of the Life of Olaudah Equiano |
| 1790-1794 | 1790 First American cotton mill.
1791 Washington, D. C. established as U. S. capital. 1794 Whiskey Rebellion breaks out in western Pennsylvania among farmers who oppose the collection of the tax on liquor and stills. 1794 Jay's Treaty provides for withdrawal of British forces from the Northwest Territory by 1 June 1796 in exchange for payments of war debts to British citizens. It is ratified on 24 June 1795. |
1790 Judith Sargent Murray, "On the
Equality of the Sexes"
1791 Susannah Rowson, Charlotte: A Tale of Truth 1792 Bunker Gay, A Genuine and Correct Account of the Captivity, Sufferings, and Deliverance of Mrs. Jemima Howe (captivity narrative) 1793 Elihu Hubbard Smith publishes anthology American Poems, Selected and Original. It includes several poems by the Connecticut Wits: Joel Barlow, Timothy Dwight, Lemuel Hopkins, and John Trumbull 1793 John Woolman, A Word of Remembrance and Caution to the Rich (calls for social reforms, including the abolition of slavery) 1793 The Hapless Orphan; or, Innocent Victim of Revenge by "an American Lady" 1794 Timothy Dwight (1752-1817), Greenfield Hill |
| 1795-1799 | 1795. 3 August. In the Treaty
of Greenville, twelve Ohio tribes turn over lands to General Anthony Wayne
after their defeat in the Battle of Fallen Timbers in 1794.
1796. 1 June. Tennessee is admitted to the Union as a slave-holding state. 17 September. Washington publishes his Farewell Address; it states his reasons for returning to private life and deciding not to run for a third term as president. 7 December. John Adams (Federalist party) wins the presidency and Thomas Jefferson (Democrat-Republican) becomes vice president in the nation's third presidential election. 1797. A cast-iron plow is invented, but farmers fear it will poison the soil and refuse to use it. 18 October. Amid tensions between the US and France, French foreign minister Tallyrand's agents suggest a "loan," essentially a bribe, to bring the French to the bargaining table. Charles C. Pinckney, the American minister to France, refuses, saying, "Millions for defense, but not one cent for tribute." The USS Constitution ("Old Ironsides") is launched as part of the new US navy. 1798. The passing of several Alien and Sedition Acts draws fire when Benjamin Franklin Bache, the grandson of Benjamin Franklin, is arrested for libeling President Adams. Thomas Jefferson later pardons all those convicted under the Sedition Act, many of whom were Democrat-Republicans. Congress abolishes debtors' prisons. 1799. George Washington dies at Mount Vernon. |
1798 Charles Brockden Brown, Wieland;
or, the Transformation (September) and Alcuin, a Dialogue
(April)
1799 Charles Brockden Brown, Arthur Mervyn; or, Memoirs of the Year 1793 (May) and Ormond; or, the Secret Witness (February) |
| Related
Timelines |
For a more comprehensive chronology of historical
events in this period, visit these sites.
|